VELscope® Oral Cancer Screening in Vancouver
Early Detection Saves Lives
At Cambie Marine Gateway Dental, we prioritize your overall health, not just your teeth. That is why we offer VELscope® oral cancer screening as part of our comprehensive approach to preventive dental care. Early detection is the key to successful treatment, and with the advanced VELscope® technology, we can help identify abnormal changes in oral tissues at their earliest stages.
What is VELscope®?
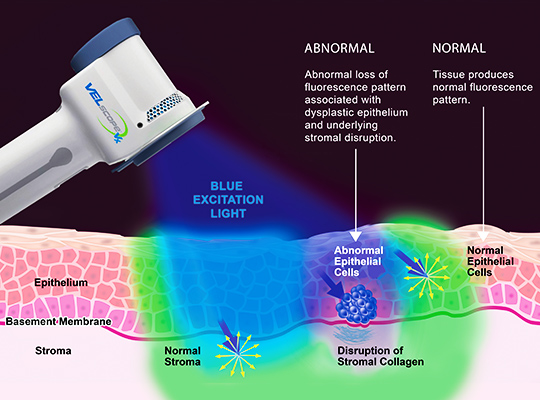
The VELscope® device uses a harmless, bright blue light to inspect the tissues of your mouth and tongue. This technology enhances our ability to detect abnormal tissue changes that may not be visible under traditional white light examination.
When the blue-spectrum light is applied, healthy oral tissues fluoresce in a distinctive way. Any disruptions in the fluorescence pattern can indicate potential issues, such as precancerous lesions or early-stage oral cancer.
VELscope® screening is safe, quick, and non-invasive, providing an important layer of protection during your routine dental visits.
Why Oral Cancer Screening Matters
Oral cancer often begins as a small white or red spot or a sore inside the mouth. Many of these early signs go unnoticed without a professional screening.
Key facts about oral cancer:
- Early detection significantly increases survival rates.
- Studies show only half of patients diagnosed with oral cancer survive beyond five years if not detected early.
- Routine screenings can catch abnormalities before they become life-threatening.
During your oral cancer screening, we carefully examine your mouth and tongue. If we spot any suspicious areas, we may perform a simple brush biopsy to collect cells for laboratory testing. Early intervention can prevent serious health complications.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Be aware of the following warning signs:
- A sore that bleeds easily or does not heal
- Changes in gum color
- Lumps, thickened areas, or rough spots
- Pain, tenderness, or numbness in the mouth or lips
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking
- Changes in how your teeth fit together
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to schedule an examination promptly.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Certain lifestyle and environmental factors increase your risk, including:
- Tobacco use (smoking or chewing)
- Alcohol use, especially when combined with smoking
- Prolonged sun exposure (risk factor for lip cancer)
- Being over the age of 40
How to Lower Your Risk
You can help reduce your risk of oral cancer by:
- Stopping or reducing tobacco use
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Using high SPF lip balms or sunscreens to protect your lips from UV exposure
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Scheduling regular dental checkups that include oral cancer screenings
Book Your VELscope® Oral Cancer Screening Today
Protect your health with a simple, non-invasive VELscope® oral cancer screening at Cambie Marine Gateway Dental in Vancouver. Early detection saves lives. Let us help you take a proactive approach to your well-being.
